
These six files are three paired-end samples from the batch condition Upload the sequence data by pasting the following links into the text.Click on the Paste/Fetch data button on the In the tool panel located on the left, under Basic Tools select Getĭata > Upload File.Select (tick) all of the files and click To History, and choose as Datasets, then Import.Īlternatively, if you are using your own personal Galaxy server or a different Galaxy server, you can import If you are using Galaxy Australia, go to Shared Data > Data Libraries in the top toolbar, and select Galaxy Australia Training Material: RNA-Seq: Yeast RNA-Seq. Import the RNA-seq data for the workshop. Alternatively, if you already have an account, login by clicking User > Login.Ģ. Register as a new user by clicking User > Register on the top dark-grey bar.Recommended browsers include Firefox and Chrome. For example, you could use Galaxy Australia. Open a browser and go to a Galaxy server.Register as a new user in Galaxy if you don’t already have an account ¶ This has implications, as discussed in section 8.
We have extracted chromosome I reads from the samples to make the There are 6 samples in total– two treatments with
#Geneious tutorial conver to bam file archive#
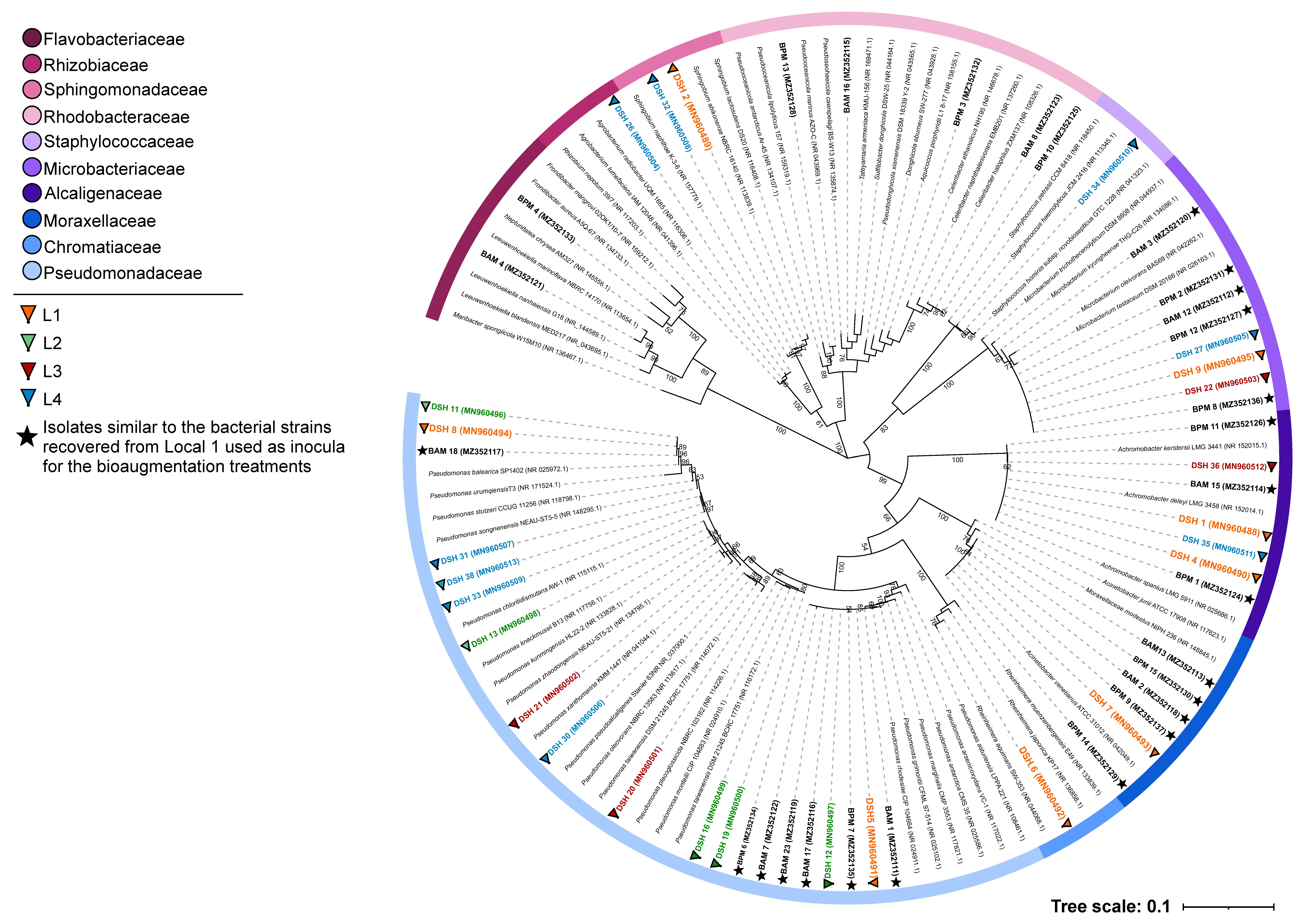
The RNA-Seq data has been uploaded in NCBI, short read archive (SRA), withĪccession SRS307298. which studies S.cerevisiae strain CEN.PKġ13-7D (yeast) under two different metabolic conditions: glucose-excess (batch) RNA-Seq-based transcriptome analysis from reads to differential gene expressionĪnd cross-comparison with microarrays: a case study in SaccharomycesĬerevisiae by Nookaew et al. The data for this tutorial is from the paper, A comprehensive comparison of It is recommended to have some familiarity of RNA-seq before beginning thisīackground ¶ Where does the data in this tutorial come from? ¶ This tutorial builds on top of the basic RNA-seq DGE tutorial. In this tutorial we compare the performance of three statistically-based RNA-Seq Differential Gene Expression: Advanced Tutorial ¶Īuthors: Mahtab Mirmomeni, Andrew Lonie, Jessica Chung Molecular Dynamics - Building input files, visualising the trajectory Molecular Dynamics - Introduction to cluster computing Identifying proteins from mass spectrometry data Section 7: How much concordance is there between methods? Filter out the significant differentially expressed genes. Generate a list of differentially expressed genes using DESeq2ģ. Extract the significant differentially expressed genes.ġ.
Examine the outputs from the previous stepģ. Generate a list of differentially expressed genes using edgeRĢ. Run Cuffdiff to identify differentially expressed genes and transcripts
Visualise the aligned reads with JBrowseġ.
Map/align the reads with Tophat to the S. Import the RNA-seq data for the workshop.ġ. Register as a new user in Galaxy if you don’t already have an accountĢ. Where does the data in this tutorial come from?ġ. RNAseq differential expression tool comparision (Galaxy) Introduction to Metabarcoding using Qiime2 Hybrid genome assembly - Nanopore and Illumina Introduction to de novo genome assembly for Illumina readsĭe novo assembly of Illumina reads using Velvet (Galaxy)ĭe novo assembly of Illumina reads using Spades (Galaxy) Introduction to de novo assembly with Velvet If exporting paired reads in fasta format, an option to export the forward and reverse reads to separate files is available by choosing ’Fasta Paired Files’ as the file type option.Common Workflow Language for Bioinformatics Phylip, FASTA, NEXUS, Newick, MEGA, Geneiousĭocuments imported in any chromatogram or molecular structure format can be re-exported in that format as long as no changes have been made to the document.īoth fasta and fastq files can be exported in compressed (fasta.gz and fastq.gz) format for smaller file size. Phylip, FASTA, NEXUS, MEGA, Phrap ACE, SAM/BAM, Geneious FASTA, Genbank (XML or flat), CSV/TSV, Geneious


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
